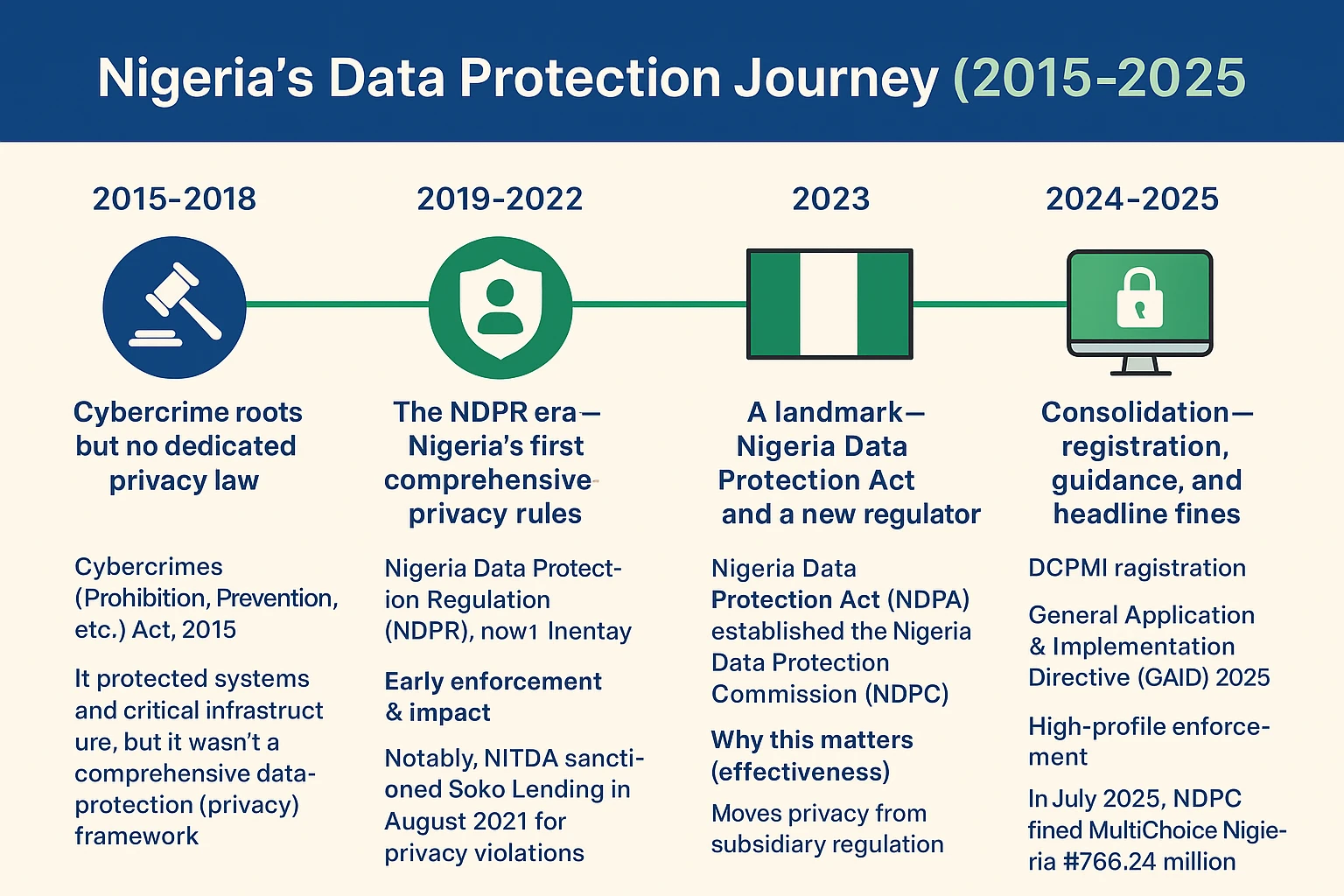
Data has become one of the most valuable assets in the digital economy, and its protection is now a global priority. For Nigeria, where digital transformation is accelerating in sectors like banking, telecoms, health, and e-commerce, robust data privacy practices are no longer optional. While the country has made remarkable strides with instruments such as the Nigeria Data Protection Regulation (NDPR) in 2019 and the Nigeria Data Protection Act (NDPA) in 2023, much of the momentum and direction has been influenced by international organizations. Among these, ISACA—a global professional association for IT governance, risk management, and cybersecurity—stands out as a thought leader shaping how Nigerian professionals and institutions approach data privacy.
The Global Context of Data Privacy
International organizations have been instrumental in harmonizing privacy practices across borders. The European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) set the global benchmark, prompting many countries—including Nigeria—to design frameworks that ensure secure and ethical handling of personal data. Similarly, organizations like ISACA, the International Association of Privacy Professionals (IAPP), and the OECD contribute by creating global standards, frameworks, and training programs.
For Nigeria, these global influences have not only informed legislative choices but also accelerated professional awareness and capacity-building.
ISACA’s Role in Nigeria’s Data Privacy Landscape
1. Capacity Building and Professional Certification
ISACA provides globally recognized certifications such as Certified Information Security Manager (CISM), Certified in Risk and Information Systems Control (CRISC), and Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA). These certifications are widely respected in Nigeria and equip professionals with the knowledge to implement, audit, and oversee compliance with data privacy laws.
Through local ISACA chapters, Nigerian IT auditors, risk managers, and data protection officers gain access to workshops, seminars, and continuing education tailored to emerging privacy challenges. This creates a workforce capable of implementing both Nigerian and international best practices.
2. Frameworks and Best Practices
One of ISACA’s most influential contributions is the COBIT framework, which guides organizations in aligning IT processes with business objectives, risk, and compliance requirements. In Nigeria, COBIT has been adopted by financial institutions, regulators, and government agencies to create structures for governance that integrate privacy obligations.
By adapting these frameworks, Nigerian organizations avoid the pitfalls of fragmented compliance and instead develop holistic strategies that balance innovation, customer trust, and legal obligations.
3. Bridging Global Standards and Local Context
While Nigeria’s NDPA draws inspiration from the GDPR, ISACA helps professionals translate these global requirements into practical, locally relevant strategies. Through its thought leadership, ISACA provides guidance on issues such as:
-
Cross-border data transfer and compliance with international adequacy standards.
-
Third-party risk management, which is vital in Nigeria’s fintech and telecom sectors.
-
Cyber-resilience frameworks to address the overlap between privacy and security.
This bridging role ensures that Nigerian businesses remain competitive globally while adhering to local rules.
4. Advocacy and Community Building
ISACA chapters in Nigeria serve as advocacy groups, sensitizing organizations about the importance of data protection beyond compliance. They encourage companies to view privacy as a trust enabler rather than a legal burden. By fostering a community of professionals, ISACA promotes peer learning and strengthens Nigeria’s overall privacy ecosystem.
The Impact of International Influence on Nigerian Privacy Laws
The NDPR (2019) and NDPA (2023) reflect not only local realities but also international benchmarks. Some examples of influence include:
-
Principles of lawfulness, fairness, and accountability—mirroring GDPR and reinforced by ISACA training.
-
Risk-based oversight models, inspired by international frameworks that emphasize proportionality.
-
Data protection officers (DPOs) as a mandatory role for high-impact organizations—popularized by global privacy practices and supported by ISACA’s professional development programs.
These influences have improved Nigeria’s ability to attract foreign investment, assure international partners, and protect citizens in a digitally connected economy.
Challenges Ahead
Despite progress, Nigeria still faces challenges:
-
Low public awareness of privacy rights.
-
Uneven compliance among small and medium enterprises (SMEs).
-
Capacity gaps in government institutions managing national identity and digital infrastructure.
Here, ISACA’s continued presence is critical—building professional expertise, promoting accountability, and helping to embed privacy by design into every level of Nigerian organizations.
A Way Forward
The past decade has proven that Nigeria’s data protection journey cannot be separated from global standards and international organizations. ISACA, through its frameworks, certifications, and community-building, has positioned itself as a key enabler of Nigeria’s progress.
As Nigeria consolidates the Nigeria Data Protection Commission (NDPC) and begins enforcing the NDPA, the need for globally aligned but locally adapted best practices will only grow. With ISACA’s continued influence, Nigerian organizations can transform data privacy from a regulatory checkbox into a driver of trust, innovation, and sustainable growth.



Comments: