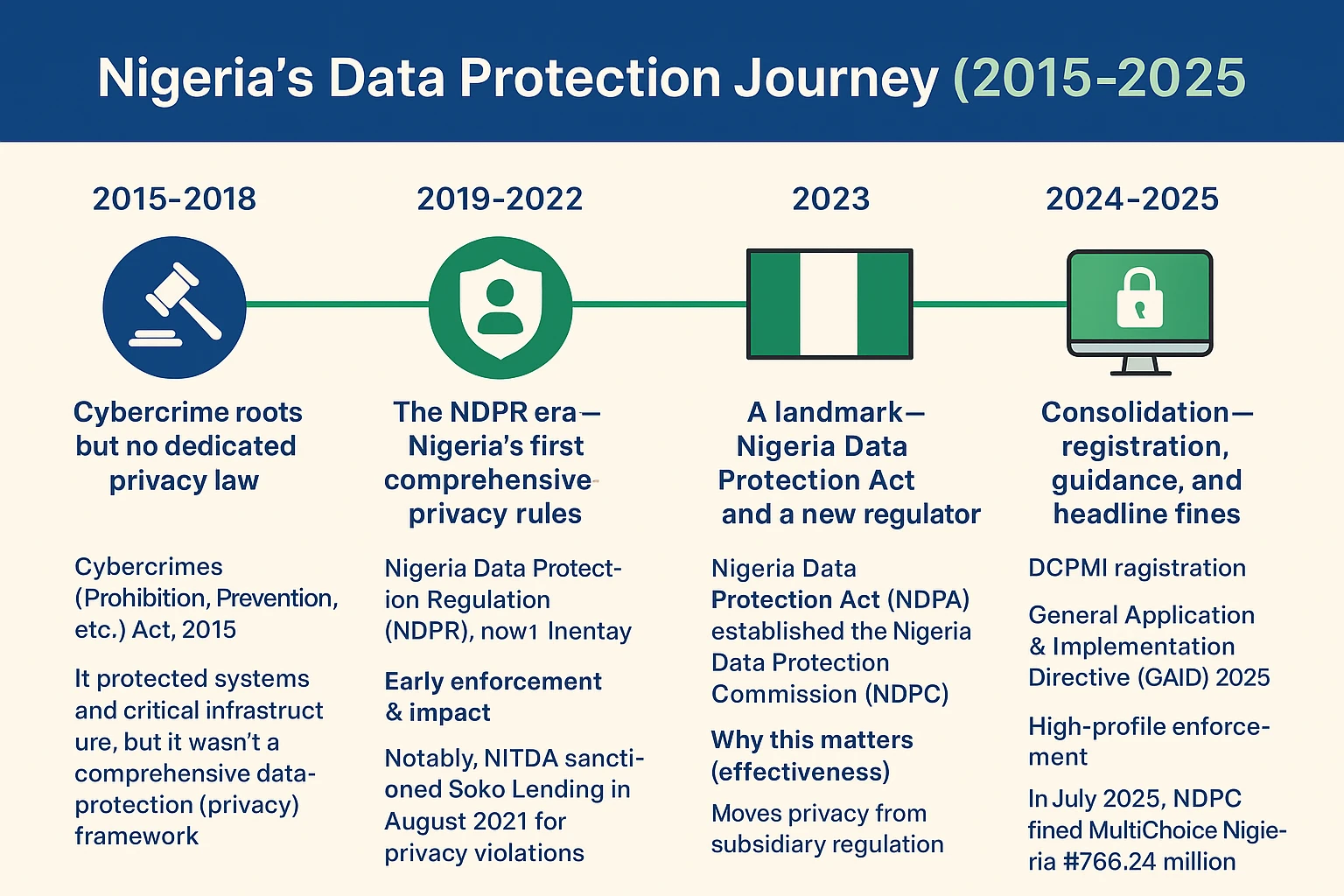
In today’s digital landscape, data security isn’t just a technical requirement it’s a legal obligation. With the enactment of the Nigeria Data Protection Act (NDPA) 2023, every organization handling personal data must adopt robust security practices like encryption and access controls to prevent breaches, protect privacy, and avoid stiff penalties.
Whether you’re a large enterprise or a small business, here’s a practical guide to securing your data, staying compliant, and safeguarding your reputation.
Why Encryption and Access Controls Are Non-Negotiable
The NDPA requires organizations to implement “appropriate technical and organizational measures” to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of personal data. These measures aren’t mere checkboxes they directly protect organizations against risks like unauthorized access, data theft, and breaches.
A stark reminder came from Nigeria’s health data leak, which exposed tens of thousands of records due to weak security controls. Such incidents highlight the urgent need for businesses to strengthen their data defenses.
Encryption and access controls have become fundamental requirements in the digital age—particularly under Nigeria’s Data Protection Act (NDPA) 2023. The Act obligates all organizations handling personal data to implement appropriate technical and organizational measures that ensure data confidentiality, integrity, and availability. Among these measures, encryption and access controls stand out as core mechanisms for protecting sensitive information from misuse or unauthorized access.
Without proper data protection practices, organizations expose themselves to significant legal and financial risks. The NDPA empowers the Nigeria Data Protection Commission (NDPC) to impose penalties of up to ₦10 million or 2% of an organization’s global turnover, whichever is greater, for violations of its security standards. Beyond fines, non-compliance may trigger investigations, sanctions, and reputational fallout that could severely impact public trust and business operations.
Real-world data breaches highlight the importance of encryption and access controls. In recent years, incidents such as Nigeria’s health data leak—where tens of thousands of personal records were exposed—have underscored the damage that weak security systems can cause. These breaches are not always the result of sophisticated cyberattacks; often, they stem from poorly configured systems, lack of access restrictions, or unencrypted data storage.
Encryption plays a critical role by making data unreadable to unauthorized users, even if they gain access to the files. It protects data both at rest (when stored) and in transit (when being shared or transmitted). Meanwhile, access control ensures that only individuals with the appropriate permissions can view, modify, or interact with sensitive information. Together, these tools create a layered defense strategy that limits internal and external threats.
In today’s regulatory environment, overlooking these protections is not just a technical oversight—it’s a business liability. Encryption and access controls are no longer optional features reserved for large enterprises; they are now standard expectations for any entity that processes personal data. Implementing them effectively helps organizations comply with legal standards, safeguard consumer data, and build lasting trust with clients, partners, and regulators alike.
Key Measures: What Your Organization Should Be Doing
Encryption
Encryption is a fundamental safeguard for ensuring data privacy and regulatory compliance. Organizations must encrypt both data at rest and data in transit using strong, industry-accepted protocols. For example, AES-256 is ideal for encrypting stored data, while TLS (Transport Layer Security) or SSL should be used for securing data during transmission. These techniques help render the data useless to unauthorized users in the event of a breach. Equally important is deploying a robust key management system—this involves storing encryption keys securely, rotating them on a regular schedule, and granting access only to trusted and authorized personnel.
For added protection, especially when dealing with sensitive personal or financial information, techniques like tokenization and pseudonymization can be implemented. These methods obscure or replace real data with artificial identifiers, making it practically worthless if accessed by malicious actors. This added layer of abstraction significantly reduces the impact of any potential data breach.
Access Controls
Restricting access to data is equally critical. Organizations should implement Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) and Access Control Lists (ACLs) to ensure that employees only access the specific data required for their roles. This principle of least privilege minimizes the risk of internal misuse or accidental exposure of sensitive information. Every access point should require secure login credentials, and organizations must enforce strong password policies to guard against brute-force attacks or credential stuffing.
Moreover, Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) or even Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) should be standard practice, particularly when accessing sensitive systems or data remotely. These authentication layers add a significant barrier to unauthorized access attempts, even if login details are compromised.
Monitoring and Maintenance
Maintaining access controls also means regular audits. Organizations must continuously review user access, especially when employees change roles or exit the company. Failing to revoke former users’ credentials introduces a persistent vulnerability that can be exploited. Audit trails and monitoring systems should be in place to log who accessed data, when, and for what reason. These logs are not only crucial for investigating incidents but also for demonstrating compliance during regulatory audits or internal reviews.
Step-by-Step Guide to Securing Your Data
1. Data Audit & Classification
The first step toward securing your organization’s data is conducting a thorough data audit. This involves mapping how data flows across your systems, identifying where sensitive personal data is stored, and evaluating the potential risks associated with each data type. Classification helps prioritize protection based on the level of sensitivity, ensuring that high-risk information receives appropriate security attention in line with the Nigeria Data Protection Act (NDPA) 2023.
2. Deploy Encryption Tools
Once sensitive data is identified, the next priority is to protect it using strong encryption methods. Encryption should be applied both to data at rest (stored in databases or backups) and data in transit (being transferred across networks). Implement industry-standard protocols such as AES-256 for data storage and TLS/SSL for data transmission to ensure information is unreadable to unauthorized users.
3. Implement Key Management
Encryption is only effective if its cryptographic keys are managed securely. Organizations must store encryption keys in protected environments, limit access to authorized personnel, and rotate keys regularly—especially when roles change or compromise is suspected. Keeping detailed logs of key usage also ensures accountability and supports audit readiness.
4. Establish Access Controls
Access to personal data should be tightly controlled through systems like Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) and multi-factor authentication. Define user roles clearly and ensure that each staff member only has access to the information necessary for their responsibilities—following the principle of least privilege. Two-factor authentication (2FA) adds an extra layer of security to prevent unauthorized logins.
5. Continuous Monitoring & Auditing
Security is not a one-time task—it requires constant oversight. Organizations should monitor all data access activities using audit logs and automated alerts. Periodic security audits help identify vulnerabilities, detect anomalies, and ensure ongoing compliance with NDPA requirements. Monitoring also provides visibility into how data is handled across your organization.
6. Train Employees
Human error is one of the most common causes of data breaches. To mitigate this, organizations should provide ongoing training to employees on data protection best practices, privacy awareness, phishing detection, and breach response protocols. Tailoring training to staff roles ensures that each team understands their responsibilities in protecting sensitive data.
7. Conduct Regular Reviews
Finally, data protection strategies should be revisited regularly to stay current with evolving threats and regulatory changes. Conduct internal reviews at least annually—or more frequently for high-risk organizations—to assess the effectiveness of your encryption, access controls, and staff compliance. Updates should be made proactively to close security gaps before they become liabilities.
5 Best Practices for Data Security Compliance
Encrypt Everything
To meet data security standards and protect sensitive information, encryption must be applied comprehensively. This includes encrypting data at rest (stored data), in transit (during transfer), and in backups. Use industry-standard encryption protocols such as AES-256 and TLS to ensure data remains unreadable to unauthorized users, even if intercepted or accessed.
Enforce Least-Privilege Access
Implement the principle of least privilege, which means users are granted only the minimum level of access needed to perform their job functions. This significantly limits the chances of accidental or malicious data exposure. Use tools like role-based access control (RBAC) and access control lists (ACLs) to enforce strict boundaries around data.
Rotate and Secure Encryption Keys
Encryption is only as strong as the protection of its keys. Organizations should rotate encryption keys regularly—ideally monthly or quarterly—and store them in secure, access-controlled environments. Implement logging for all key usage and restrict access to only those with specific authorization.
Log and Audit All Access Events
Keeping detailed logs of every access event allows for real-time monitoring and retrospective analysis of data interactions. Frequent auditing of these logs helps detect unusual patterns or potential breaches early. This not only boosts internal oversight but also supports accountability and compliance during regulatory inspections.
Educate Your Workforce Continuously
Human error is a leading cause of data breaches. Ongoing staff training on topics like phishing awareness, data handling procedures, and incident response is essential. Tailor education efforts to employee roles and update them regularly to reflect current threats and compliance requirements, such as those outlined in Nigeria’s NDPA 2023.
Understanding Your NDPA Obligations
Organizations that fail to meet NDPA standards face serious repercussions:
-
Fines of up to ₦10 million or 2% of global turnover, whichever is higher.
-
Reputational damage that can erode customer trust and impact revenue.
-
Mandatory obligations like appointing a Data Protection Officer (DPO), registering with the Nigeria Data Protection Commission (NDPC), and conducting regular audits for major data processors.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Is encryption mandatory under the NDPA?
Yes. The Nigeria Data Protection Act (NDPA) mandates encryption as a fundamental data protection measure, especially for sensitive and personally identifiable information (PII). Organizations are required to adopt technical safeguards such as encryption to ensure confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data during storage, transmission, and processing. Failure to encrypt sensitive data could be considered a breach of compliance.
2. How often should encryption keys be rotated?
Industry best practices recommend that encryption keys be rotated either monthly or quarterly, depending on the sensitivity of the data and the risk environment. Additionally, key rotation should be performed immediately after a change in user roles, following a security incident, or whenever there is any indication that the key may have been exposed. Regular rotation minimizes the risk of keys being compromised and strengthens the overall encryption framework.
3. Are access controls optional for small and medium enterprises (SMEs)?
No. Access controls are mandatory for all organizations handling personal data, regardless of their size or industry. SMEs must implement role-based access control (RBAC), enforce the principle of least privilege, and use tools like multi-factor authentication (MFA) to safeguard data. The NDPA does not exempt smaller organizations from meeting security obligations, and failure to do so can result in regulatory penalties.
4. What happens if we don’t comply with the NDPA?
Non-compliance with the NDPA can lead to serious consequences. These include heavy financial fines, lawsuits, reputational damage, and even business closure in extreme cases. The Nigeria Data Protection Commission (NDPC) has the authority to investigate breaches, impose sanctions, and compel organizations to implement corrective actions. Compliance is not just a legal necessity—it is essential for earning and maintaining public trust.
Final Thoughts
Encryption and access controls are not optional—they are foundational to both compliance and trust. By embedding these practices into your data protection strategy, you not only fulfill your legal obligations under the NDPA but also build resilience against data breaches.
If your organization needs assistance with setting up secure systems, preparing for an NDPC audit, or conducting a Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA), consider consulting experts.
👉 Contact Headspace (Stephen Alaekwe & Co.)—licensed, NDPC-accredited data protection specialists ready to help you navigate compliance confidently.




Comments: